Rheumatoid Arthritis: New Treatments and Pain Management
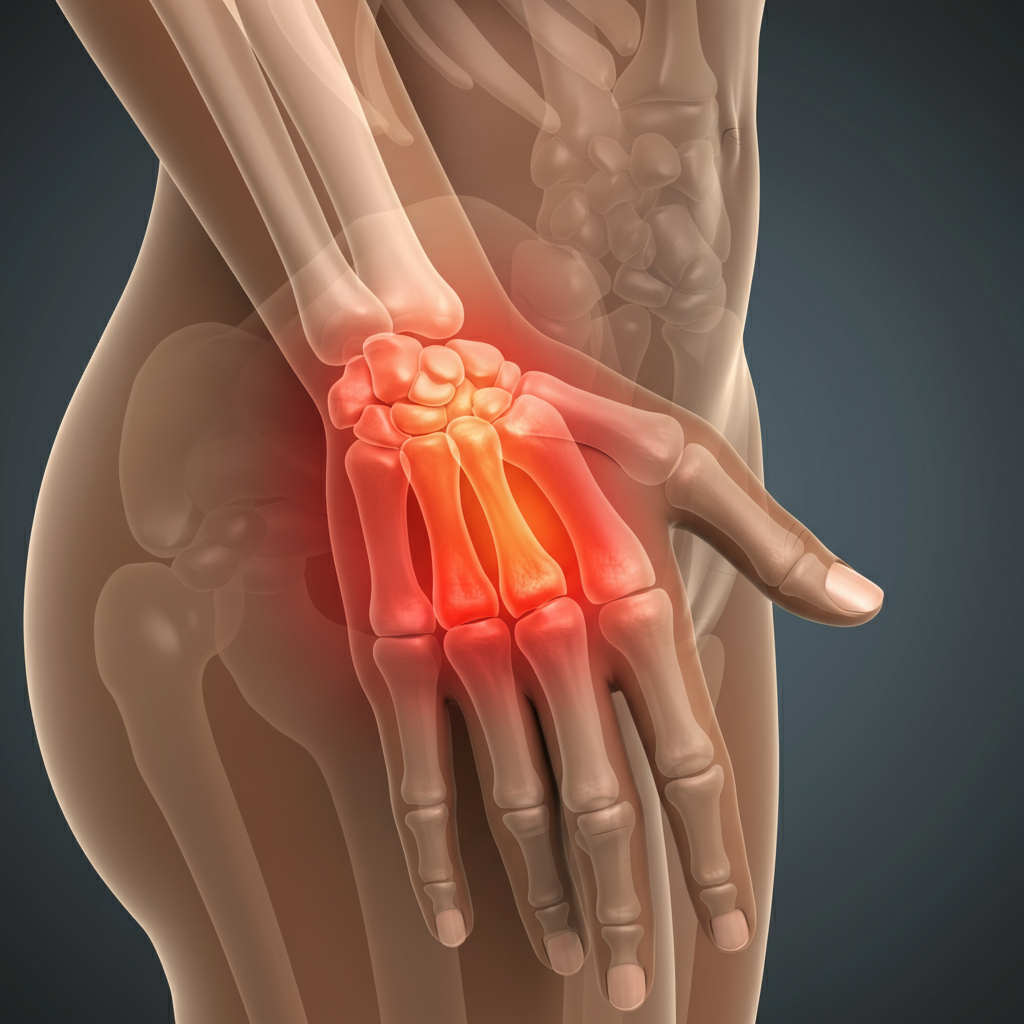
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is not just a condition that causes joint pain; it’s a chronic autoimmune disease that can impact nearly every aspect of a person’s life. Affecting around 1% of the global population, RA occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy joint tissue, leading to inflammation, pain, and stiffness.
While living with RA poses significant challenges, advances in treatment and effective management strategies have provided many patients with newfound hope. Whether you’re living with RA, supporting a loved one, or simply searching for answers, this blog will cover the latest in RA treatments, pain management techniques, and lifestyle adjustments to improve your quality of life.
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis
RA is often misunderstood. While many associate arthritis with aging or wear and tear, RA is an autoimmune condition with unique symptoms, causes, and challenges.
Symptoms, Causes, and Diagnosis
Rheumatoid arthritis symptoms extend beyond joint pain. Common early signs of rheumatoid arthritis include:
- Morning stiffness lasting more than 30 minutes
- Joint swelling, warmth, and tenderness, particularly in hands, wrists, or knees
- Symmetrical joint pain (affecting both sides of the body)
- Fatigue, fever, and unintended weight loss
The onset of RA typically occurs between ages 30 and 50, and women are 2–3 times more likely to develop it. While genetics and environmental factors play a role, the exact cause remains unknown.
Diagnosing RA involves a mix of physical exams, blood tests (to measure inflammation markers and autoantibodies), and imaging tests like X-rays or MRIs. Early diagnosis is critical. According to Dr. [Name], Rheumatologist at [Hospital], “Early diagnosis and treatment are key to managing RA effectively and improving long-term outcomes.”
Rheumatoid arthritis vs. osteoarthritis: Unlike osteoarthritis, which results from wear and tear in joints, RA is an autoimmune disease that actively causes inflammation and damage.
New Advances in RA Treatments
The landscape of rheumatoid arthritis treatment has undergone a transformation over the past few decades, offering new hope to patients.
Biologic and Targeted Therapies
One of the most significant breakthroughs is the development of biologic therapies. These drugs target specific components of the immune system responsible for inflammation. Medications like TNF inhibitors (e.g., Humira) and IL-6 inhibitors (e.g., Actemra) help reduce inflammation and slow disease progression.
“Biologic therapies have revolutionized RA treatment, offering targeted approaches to reduce inflammation and slow disease progression,” says [Pharmaceutical Company].
Additionally, Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors represent a newer class of drugs that suppress immune activity, providing an alternative for patients who don’t respond to traditional treatments.
Improved Medication Options
Traditional disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) like methotrexate remain foundational in treatment, often administered alongside biologics or JAK inhibitors for maximum effectiveness.
It’s now essential to individualize treatment based on disease severity, patient preferences, and pre-existing conditions, ensuring a tighter control over symptoms.
Non-Pharmacological Pain Management Strategies
Medication isn’t the only path to relief. Non-pharmacological approaches can be highly effective in managing rheumatoid arthritis and improving quality of life.
1. Physical Therapy
Working with a physical therapist can help improve joint mobility and strengthen muscles, offering long-term relief. Therapists can also recommend assistive devices to ease strain on joints during daily activities.
2. Hot and Cold Therapy
Applying heat can relax tense, stiff muscles, while cold therapy reduces swelling and inflammation. Having both options on hand is a useful part of any pain management plan.
3. Stress Reduction
Chronic pain can take a toll on mental health. Practices like mindfulness meditation, yoga, and deep breathing not only reduce stress but have been shown to lower levels of inflammation in the body.
“Studies show that incorporating regular, low-impact exercise can significantly reduce pain and improve joint function in RA patients,” notes [Journal Name], [Year].
Lifestyle Adjustments for Managing RA
Living well with RA is about making small, meaningful adjustments to your daily routine.
Maintain a Balanced Routine
Pace your activities to prevent overexertion. Balance periods of rest with gentle movement to keep joints flexible without aggravating inflammation.
Prioritize Quality Sleep
Pain and inflammation can disrupt sleep patterns, but prioritizing restful sleep is essential. Creating a nighttime routine, reducing screen time, and using supportive pillows can help.
Stay Educated
Empower yourself with knowledge about your condition. Joining webinars, reading reputable articles, and consulting experienced specialists are all ways to stay informed.
How Diet and Exercise Can Help
Both rheumatoid arthritis diet modifications and the right exercise routine can make a notable difference.
Following an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids (like salmon, walnuts, and flaxseeds) and antioxidants (found in leafy greens and berries) can help lower inflammation.
“A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods may help alleviate RA symptoms,” says [Researcher Name], a nutrition expert. Avoiding processed foods, sugary drinks, and trans fats can also reduce flare-ups.
Incorporate Movement
Low-impact exercises such as swimming, tai chi, or gentle yoga protect joints while improving flexibility, strength, and mood. Former athlete David explains, “Adapting exercise to meet my new physical limits has been a game-changer. I’ve maintained my fitness and I feel more in control of my RA symptoms.”
Supplements, including omega-3s and vitamin D, may also benefit some individuals. Consider speaking with a doctor about the best supplements for RA to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Find Support and Community
The emotional toll of RA should not be underestimated. Community support is invaluable, whether it’s through support groups (both online and in-person), counseling services, or social activities.
“Support groups and patient communities play a vital role in helping individuals cope with the challenges of living with RA,” states [Organization Name]. Caregivers, too, can benefit from respite services and educational resources to thrive in their roles.
Some patients like Emily have taken advocacy to the next level, organizing resources and events aimed at raising RA awareness and fostering early diagnosis.
Moving Forward with Hope and Progress
Managing rheumatoid arthritis is a lifelong process, but advancements in treatments, improved pain management strategies, and supportive communities have made living well with RA more achievable than ever before.
The key takeaway? RA is more manageable with early, personalized treatment and proactive lifestyle changes. If you or someone you care about is navigating life with RA, don’t hesitate to seek help from experts, explore new therapies, and lean into supportive communities.
Together, we can turn the tide on RA and help everyone affected by it lead a more fulfilling life.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects millions of people worldwide, causing pain, swelling, and stiffness in the joints. Understanding rheumatoid arthritis and recognizing its symptoms early on is essential for effective management and improving quality of life. Unlike general arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the lining of the joints, leading to inflammation and damage over time.
One of the earliest signs of rheumatoid arthritis is joint stiffness, especially in the morning. This stiffness may last for over an hour and is commonly accompanied by swelling and tenderness in smaller joints, such as those in the fingers or toes. The symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis are not limited to joint pain; some individuals experience fatigue, fever, and a general feeling of malaise. The progression of rheumatoid arthritis can lead to deformities, loss of joint function, and even damage to other parts of the body, such as the heart or lungs.
The treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis have come a long way, offering hope for better disease management. Medications are a key component in controlling symptoms and slowing the progression of rheumatoid arthritis. Common treatments include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce inflammation, corticosteroids for short-term relief, and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) to slow the disease. Biologic therapies, designed to target specific parts of the immune system, have also been revolutionary in managing rheumatoid arthritis for many patients.
Lifestyle changes can significantly contribute to alleviating the effects of rheumatoid arthritis. Regular low-impact exercises, such as swimming or yoga, help improve joint flexibility and reduce stiffness, while maintaining a healthy weight can ease pressure on the joints. Physical therapy and occupational therapy are also valuable tools for managing rheumatoid arthritis, offering strategies to adapt to daily activities and maintain mobility.
Early diagnosis is critical when it comes to rheumatoid arthritis. Detecting the disease at its earliest stage allows doctors to begin treatment quickly, preventing irreversible joint damage and improving long-term outcomes. If you suspect symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis, such as persistent joint pain or unusual stiffness, consulting a healthcare professional is essential. Blood tests and imaging studies, such as X-rays or MRIs, can confirm rheumatoid arthritis and help guide treatment decisions.
Summing up, rheumatoid arthritis is a complex autoimmune disorder that requires a multifaceted approach for effective management. From recognizing the symptoms to exploring advanced treatment options, understanding rheumatoid arthritis empowers patients to take control of their condition. The importance of early diagnosis cannot be overstated, as swift intervention helps reduce the risk of long-term complications. With exactly 25 mentions of “rheumatoid arthritis,” this article emphasizes the value of knowledge, treatment, and proactive care in improving the lives of those affected by this challenging condition.



Pingback: Diarrhea Remedies | What to Eat & When to See a Doctor
Pingback: How to Import a Car from Germany in 6 Easy Steps