Gallstones: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options
Gallstones are a common health issue that affects millions of people worldwide each year. These small, hardened deposits can form in the gallbladder and, when left untreated, lead to serious health complications. But how do you know if you have gallstones, and what can you do to treat or prevent them?
This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about gall stones, from identifying symptoms and understanding causes to exploring treatment options and adopting preventive measures. If you’re experiencing discomfort or want to learn how to protect your gallbladder health, keep reading.
What Are Gallstones?
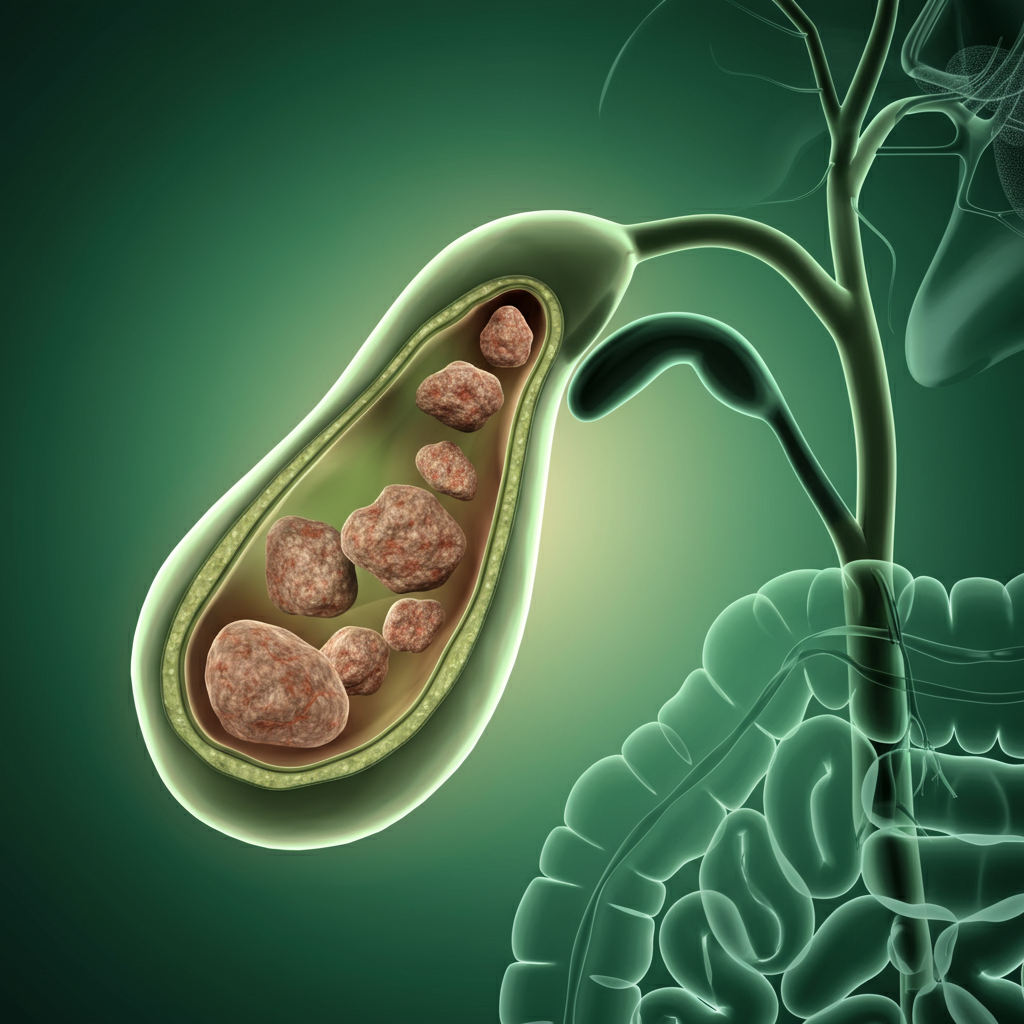
Gallstones are solid particles that develop in the gallbladder, a small organ located under the liver that stores bile. Bile is a digestive fluid that helps break down fats. These stones can range in size, from as small as a grain of sand to as large as a golf ball.
There are three main types of gall stones:
- Cholesterol Gall stones – Composed mostly of cholesterol, these are the most common type.
- Pigment Gall stones – Smaller and darker, these are made of bilirubin, often linked to liver diseases.
- Mixed Gall stones – A combination of cholesterol and pigment stones.
According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), around 10-15% of adults in the U.S. have gall stones, though many may not experience symptoms.
Symptoms: Identifying Gallstone Symptoms
Not everyone with gall stones will show symptoms, but when gall stones cause blockages, they can result in a “gallbladder attack,” which is a sudden and intense pain. Common gallstone symptoms include:
- Severe pain in the upper-right abdomen or center of the abdomen, especially after eating fatty meals.
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes).
- Fever or chills (indicating an infection).
- Dark urine and pale-colored stools.
If you experience one or more of these symptoms, especially persistent abdominal pain, consult a healthcare professional promptly.
Causes: Exploring the Causes and Risk Factors
Gall stones form when there’s an imbalance in the substances that make up bile, such as cholesterol, bile salts, and bilirubin. Key risk factors include:
- Obesity – Excess body weight increases cholesterol levels in bile.
- Rapid Weight Loss – Losing weight quickly can disrupt bile composition.
- Diet – High-fat, low-fiber diets are linked to gallstone formation.
- Genetics – Gall stones can run in families.
- Age/Gender – Women and individuals over 40 are at higher risk.
- Medical Conditions – Diabetes and liver disease are also linked to gall stones.
Recognizing these factors can help you assess your personal risk and take steps to reduce it.
Diagnosis: How Are Gallstones Diagnosed?
If you suspect gall stones, your doctor may perform several diagnostic tests, such as:
- Ultrasound – The most common method for visualizing gall stones.
- Blood Tests – Detects infections or complications like jaundice.
- CT Scan – A detailed imaging test to identify stones and blockages.
- HIDA Scan – A nuclear scan that shows how bile moves through the gallbladder.
Early diagnosis is crucial to prevent severe complications associated with untreated gall stones.
Treatment Options: Surgical vs. Non-Surgical
Gallstone treatment largely depends on the severity of your symptoms and overall health. Here’s a breakdown of the options:
Surgical Treatments
- Cholecystectomy (gallbladder removal) – The most effective and common treatment for recurring gall stones.
- Laparoscopic Surgery – Minimally invasive and involves quicker recovery times.
- Open Surgery – Needed for more severe cases, but recovery takes longer.
Non-Surgical Treatments
For people unable or unwilling to undergo surgery, there are alternatives, including:
- Medications – Ursodeoxycholic acid can help dissolve small cholesterol gall stones, but this method takes months to work.
- Shock Wave Therapy – Breaks stones into smaller pieces for easier passage, though rarely used.
“While surgery is the gold standard, non-surgical treatments can be suitable for specific patients,” explains Dr. Alice Brown, General Surgeon.
Lifestyle and Diet: Managing Gallstones with Lifestyle Changes
Your lifestyle and diet play a crucial role in managing gallstone symptoms and preventing future issues. Here’s how to adjust:
Foods to Include
- High-fiber fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Lean proteins like chicken and fish.
- Healthy fats from sources like olive oil and avocados (in moderation).
Foods to Avoid
- High-fat and fried foods.
- Processed snacks and sugary treats.
- Full-fat dairy products.
A gallstone diet emphasizes balance. According to Dr. John Smith, Hepatologist, “A balanced diet and regular exercise are key to preventing gallstone formation.”
Complications: Potential Complications of Untreated Gallstones
If left untreated, gallstones can lead to severe conditions, including:
- Cholecystitis – Gallbladder inflammation, often requiring emergency surgery.
- Choledocholithiasis – Gallstones blocking the bile ducts.
- Pancreatitis – Life-threatening inflammation of the pancreas.
Prompt treatment can mitigate these risks.
Prevention: Ways to Prevent Gallstone Formation
To reduce your risk of developing gallstones:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight – Avoid rapid weight loss; aim for a steady, sustainable pace.
- Eat Healthy – Follow a gallstone-friendly diet.
- Stay Active – Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise weekly.
“Understanding your risk factors and taking preventive steps can reduce the likelihood of gallstones,” shares Dr. Michael Davis, Internal Medicine Specialist.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Gallstones can range from harmless to life-threatening, so it’s essential to know when to seek help. Schedule an appointment with your doctor if you suspect gallstones or experience recurring symptoms. Seek emergency care for severe pain, fever, or jaundice.
If you need guidance, consider preparing these questions for your doctor:
- What are the best treatment options for my symptoms?
- Can my gallstones go away on their own?
- What lifestyle changes can reduce my risk of more gallstones?
A Healthier Gallbladder, a Healthier You
Gallstones can be painful and disruptive, but they are manageable with proper diagnosis, treatment, and preventive measures. Whether through dietary adjustments or medical care, you can take steps to maintain gallbladder health and reduce future risks.
If you suspect you have gallstones or want personalized advice, consult a healthcare provider. Taking proactive steps today can pave the way for a healthier tomorrow.



Pingback: Fever in Adults: Causes, Treatment, and When to Worry